
There is most likely no way to get a process ID (PID) of the Firefox process. The process output will be given by going to the root of your browser and typing grep Firefox ps aux. It may be preferable to use a second line *grep -v to remove that line. The word chrome appears in the output of Process 3384 because it is a ‘grep’ command. The string ‘firefox’ is used to indicate whether a process is active. Each process has the string firefox, which can be used to identify it. This is where you get the letters ‘ps aux’, which is where you get the ‘v’. Typically, you only want to know what someone’s doing or why someone is running a particular program. Most systems with multiple users receive a screenful output of ps -au via a ps -au command. The grep command can also be used to search for a specific pattern in a file when it is being viewed. Grep command can be used in a variety of ways, including specifying a file that should be searched. If you want to learn more, copy the following command and use the ps and grep command man pages, or pass the –help option.
PSEF COMMAND EXPLANATION HOW TO
Furthermore, we learn how to use pgrep to generate a list of process names and PIDs. The article teaches how to prevent ‘grep’ from appearing in PS command results on Linux, macOS, *BSD, and Unix-like systems. The first step is to figure out how to block grep from the results and outputs of a ps command. PS command output can be output by typing in grep into the command line. The ps command displays a list of active shell processes. Ps command can be used to find out everything about a running process on both Linux and Unix systems.
The ps grep command can also be used to find out what processes are running on a system, and to monitor process activity. It allows users to search for and kill processes that are consuming too much CPU or memory, or that are causing other problems. The ps grep command is a powerful tool for managing processes on a Linux system.
Data for the leader IDs of the group can be viewed in the glist option.
PSEF COMMAND EXPLANATION FULL
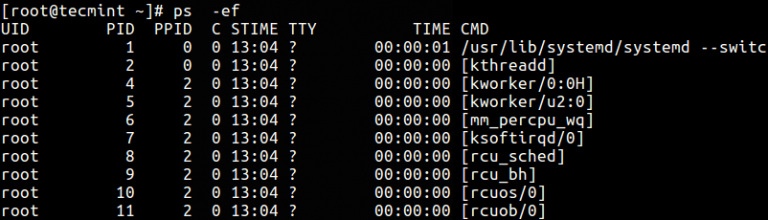
There are two options: the e option, which displays all processes, and the f option, which displays all processes in a full size. The Options option displays a list of all processes running on your system, with the exception of session leaders. The ps command can be used to view process information for all users or for a specific user. This information can be used to monitor and troubleshoot process-related issues. The ps command in Linux is a tool used to display information about the currently running processes. The ps command is a command line utility that displays or views information relating to Linux system processes. Full-format listings are those that include all of the processes’ details. The -e option allows PS to display all processes in chronological order. All processes that run on a system in standard format are printed using the “-ef” option of the “ps” command.įor UNIX, the unit is Ps -ef.

These formats are known as standard formats. In Linux Mint 20.3, the “ ps -ef” Command serves as the main interface. In addition to the simple -ef command, there is also a different output for the – ps command. This command displayed all processes running on the system as shown in the image below. All processes that were started during the current terminal session in Linux Mint 20.3 will be printed using the -ef option in the PS command with the -ps option. In this article, we will learn how to use the PS -ef command in Linux Mint 20.3. On the terminal, the p command prints all of the running processes, as well as some information. In Linux, you can query the information associated with the processes that are running by using a variety of commands. This command can also be used to kill processes that are not responding. The ps -ef command is often used to determine which processes are taking up the most CPU time or memory. The output of this command gives information on the PID ( process ID), the TTY (terminal), the TIME (cumulative execution time), and the CMD (command name). The ps -ef command in Linux is a system administration command that is used to report a snapshot of the current processes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
